VAT (value added tax) is always applicable to those who carry out trading activities.
In general, the topic of VAT accounting is quite complex, due to the detail of the various groups of goods to which it applies and the legislatively established differentiated system of tax rates. We will not go into some of the wilds of the VAT accounting policy, but we will reveal the main essence of this tax itself and its offset method in the implementation of trading operations.
VAT is an indirect tax, that is, it does not directly affect who sells their goods. Its payer is the buyer himself. The seller's participation here is indirect; he simply transfers money, in the form of tax, from the buyer to the budget.
The level of deductions (its interest rate) is set directly by the legislator himself. The state. The only economic impact of VAT directly on the seller is that it can change the price competitiveness of his product. The higher the bid, the more expensive his product is, which may force the buyer to look for an alternative to him. But, in its general form, it has a single rate for most goods and services - 20%.
For an easier understanding of VAT, the principle of its calculation and what is a tax deduction or offset, let's give a simple example.
There is an entrepreneur Petya, who is engaged in retail trade. He buys products from a wholesale supplier and sells them at retail.
As noted earlier, the VAT rate for most types of goods is 20%.
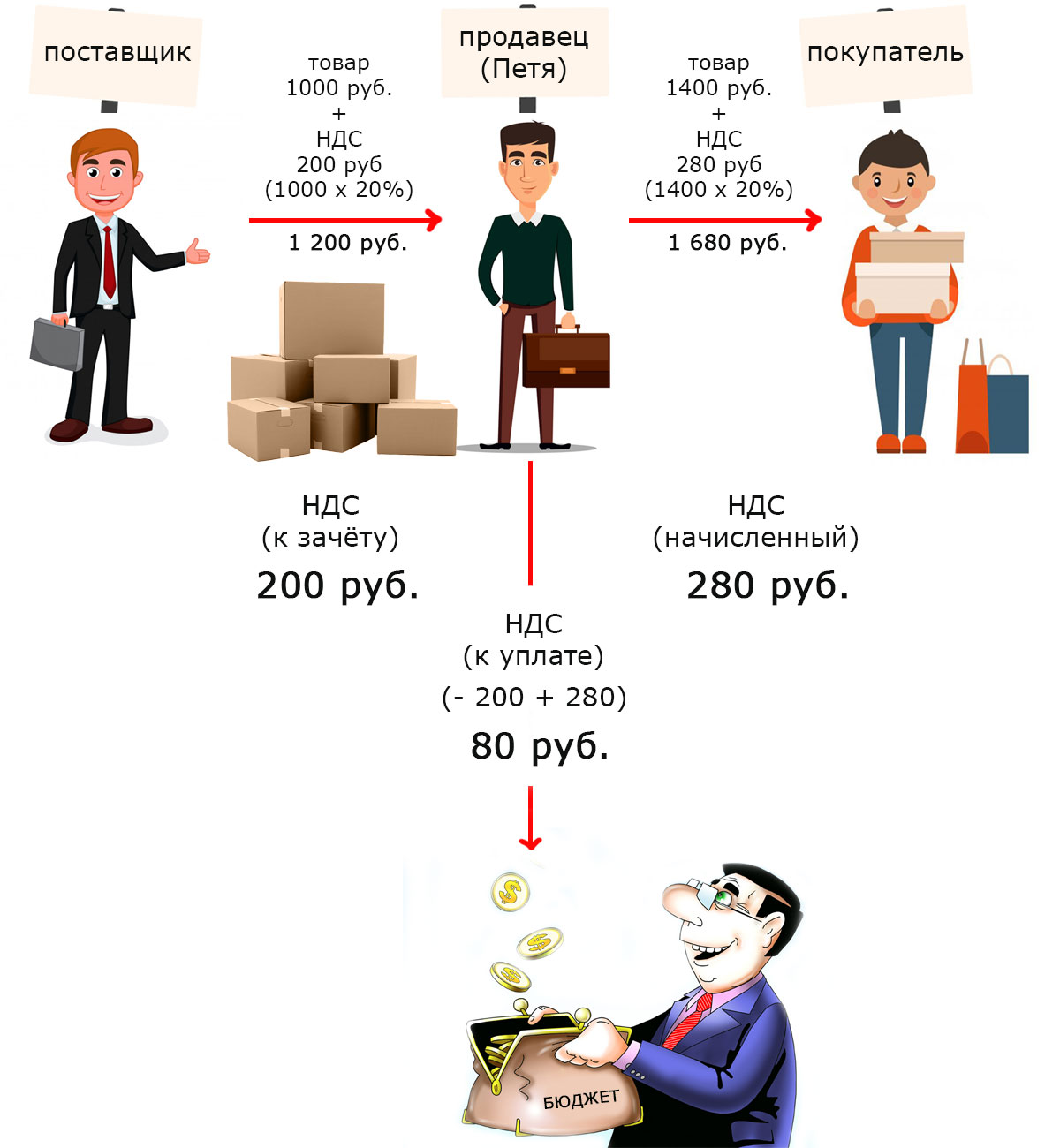
In June, Petya bought goods from a supplier for 1200 rubles. That is, the product itself is 1000 rubles. + VAT 200 rubles. Petya received from the supplier an invoice and an invoice for the amount of 1200 rubles, where a separate line is allocated VAT 200 rubles.
During the same month, Petya sold this product at its price by 1,680 rubles. That is, the product itself is 1400 rubles. + VAT 280 rubles..
A month has passed and now Petya needs to submit a tax return and pay VAT to the budget no later than the 20th of the month following the reporting one (June).
The calculation of the VAT amount required for payment is quite simple. It is necessary from the amount of VAT received in the revenue (280 rubles). deduct the amount of VAT already paid (200 rubles - for the purchased goods) in the same month (reporting). Total to be paid to the budget is 80 rubles.
That is, the VAT that Petya pays when buying his goods is usually called deductible, and the accounting method itself is a credit.
This means that during the reporting period, the organization receives VAT from customers (when it sells its products) and pays VAT when purchasing goods from suppliers (materials, energy resources, services). VAT received in revenue is accrued, and paid when buying goods, services is deductible (offset).
VAT to offset is the tax that has already been paid, so when calculating VAT to be paid to the budget, it is deducted from the VAT accrued.
VAT payable = VAT accrued – VAT (paid to suppliers – deductible)
It is not difficult to guess that if the sale of products of an organization (enterprise) is export-oriented, then there may be situations when the amount of deductible VAT is greater than the accrued one. That is, the organization pays VAT to suppliers in larger amounts than it receives in revenue, since most products are sold for export with a zero VAT rate. In this case, in the tax return, VAT payable to the budget will be marked with a minus sign. This means that the budget will have to return VAT to the organization by this amount. This is usually done by offsetting the payment of taxes by the organization in subsequent periods, or by returning funds to its settlement account.
The basis and supporting documents for VAT calculation are the supplier's primary documents (invoice and invoice with allocated VAT amounts) and sales receipts for products sold.
This is the principle of the offset method of VAT accounting, which is used for both small and large businesses.
The VAT offset method reveals the very essence of this tax!
Tax, what is it called? Right! - For added value. What in this case (from the above example) is the added value?

The added value is what Petya added (400 rubles) to what he bought. That is, the taxable base = Revenue (without VAT) minus Material costs (without VAT).
ds = In - MZ
Petya's revenue is 1400 rubles, and material costs are 1000. Petya added 400 rubles. (1400 rubles. – 1000 rubles.). This amount should be multiplied by the VAT rate of 20% and what happens should be paid to the budget.
400 rubles.x 20 % = 80 rubles.
That is, in its classical form, VAT is calculated by deducting the Added value and multiplying it by the tax rate (20%).
But, since for tax accounting, determining the amount of VAT required for payment through the calculation of value added is not the best option, then it is the offset method of its accounting that is used for its calculation.
In fact, these two methods (that through the calculation of value added, that through the offset of VAT) are identical and equally correctly deduct the amount of VAT from the value that was added by the business in the reporting period.
VAT is calculated according to the formula:
VAT = Cost of goods (cost price+ profit) x 20%
To remove VAT from the amount:
VAT = (Value of goods with VAT x 20%)/120%
That is, for example, the cost of the goods is 1000 rubles. It is necessary to charge more VAT on it.
1000 rubles x 20 % = 200 rubles.
1000 rub. + 200 rub. = 1 200 rub.
Now you need to find out how much VAT is accrued in the amount of 1 200 rubles.
(1200 rubles * 20%) / 120% = 200 rubles.
Also note that for certain groups of goods, there are VAT benefits. So, for example, in addition to the generally accepted rate of 20%, there are also rates of 10%, 7%, 5% and zero.
At the legislative level, regarding VAT, there are quite a lot of various amendments applied to various groups of goods, sellers, as well as the procedure for its accounting and payment.
For example, for products purchased from suppliers at a generally established rate and its subsequent sale without VAT (with benefits using a 0% rate), the offset method is not applicable. In such cases, VAT is not applied to the deduction, but it simply increases the value of the goods that are sold. In other words, it increases its cost.
In conclusion, we note that it is important for anyone to know what VAT is, since everyone, both individuals and legal entities, are directly involved in their daily lives, if not in its calculation, then in the payment for sure.
What is VAT and its deduction - in simple words - Something like that!



































Валерия