The first thing to understand: discounting is a calculation method or the process of converting one into another using calculated coefficients. A type of filter through which some values are passed and adjusted at the output.
The discounting method is most often used when calculating cash flows, where their assessment is made for each time interval, within the accepted calculation horizon. It is the time factor that forces us to resort to discounting, because money costs differently at different times.
Discounting is a method of simple revaluation of money, or rather their value. It is made in order to bring the value of future money to the value of today (current). I.e., the comparability of money in price is made in order to draw real conclusions about the effect obtained.
In this context, the future implies some kind of planning period (1st year, 2nd year, 3rd year, etc.), and the current – base period (0th year) relative to which this planning is carried out.

Discounting of cash flow is carried out using a discount coefficient calculated on the basis of its rate. Do not confuse the discount rate and the rate – these are different things.

To understand the very essence of this process – discounting method, let's go to an example.
The company invests $ 1,000 thousand today in the development of its business, and next year (2nd) receives a return of $ 300 thousand, then in the next (3rd, 4th and 5th) another $ 300 thousand.
As a result, what does this company have for 5 years of its investments.

With $ 1000 thousand invested, she received $ 1200 thousand. Not bad, the company is in the black (+ $ 200 thousand).
However, for an investor, this is not an objective result due to the incompatibility of the dollar price ($) at the time of their investment with the moment of their receipt in the form of income. In this case, the calculation did not take into account, at least, inflation per dollar ($) for each year (in the 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th).
Therefore, in order to get the real picture, to compare how much you invested, how much you received, and the method of discounting the cash flow during the entire billing period is used.
For these purposes, it is necessary to calculate the discount rate for each period in which money flows (outflow and inflow).
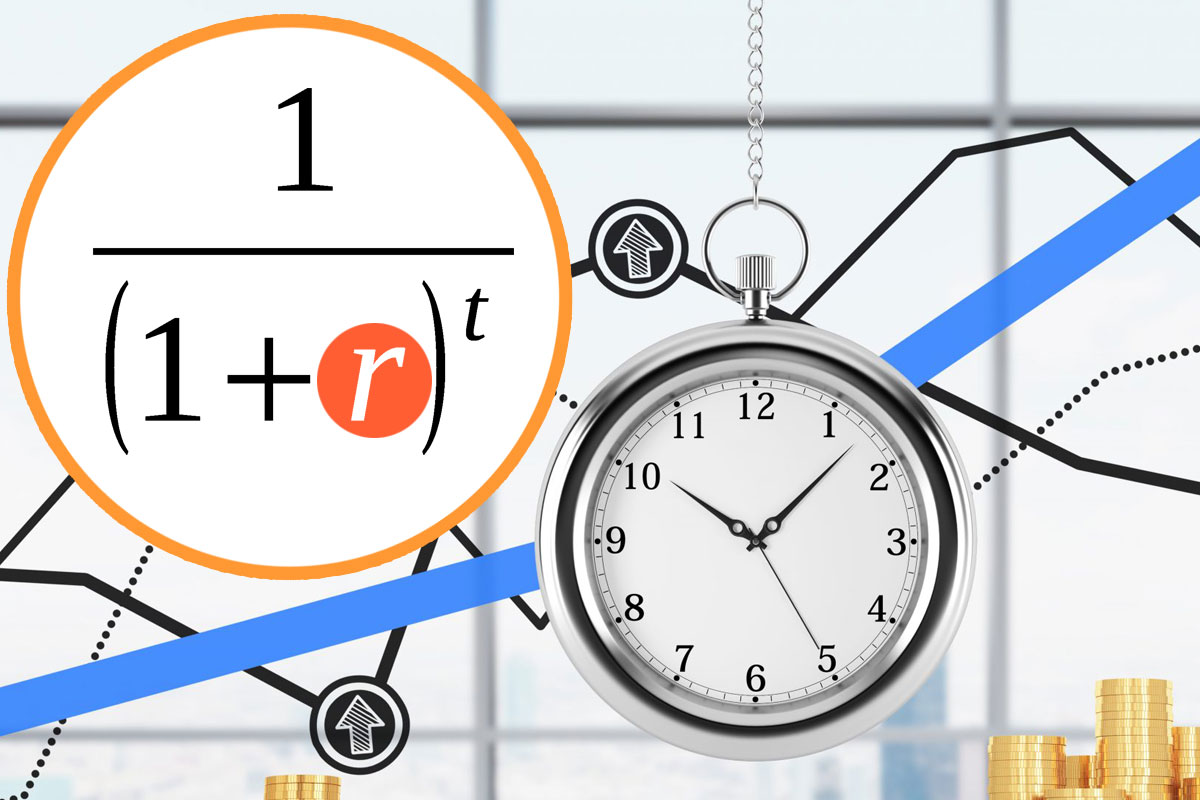
The formula for calculating the discount rate:
Kd = 1/(1 + Nd)t
Where, Hd is the discount rate (sometimes called the discount rate).
t– the time period relative to which the calculation is made.
The discount coefficient is represented by the inverse formula for calculating compound interest, which allows by multiplying it with money of a certain period, to bring them to the equivalent (to the value) of the current period.
The discount rate (Nd) includes risks associated with possible depreciation of the amount received in the future period.
Usually the minimum discount rate corresponds to the interest rate bank rate (refinancing/inflation rates) for the currency in which the calculation is made. It may also include other investor risks that may affect the depreciation of funds in the future due to factors other than inflation (falling prices, solvency, equipment downtime, etc.).

When calculating the discount rate, it must be remembered that the current period (1st), to which the value of future money will be reduced, will always be equal to 0. Or in another way, this is the start period of our investments, at which t=0. In the first period of the project implementation, the coefficient is always equal to 1 (1/(1+Nd)0), and this is natural.
Returning to our example, we will discount the received cash flow for each period, taking into account that the discount rate (risks) will correspond to the level of average annual inflation per US dollar ($) of 8%.
What does the company have in this case:

With $1,000 thousand invested, she received $ 994 thousand.
When calculating cash flow, taking into account discounting, the result is no longer the same, the company is in the red (-6 thousand $). But in this case, the value of the money of future periods is already comparable to the value of the money of the period when the investment was made (1st year). From this calculation, it can be seen that the company did not receive a real effect at the established discount rate, which indicates that the investment was not effective.
Now, we think you understand the essence of the discounting method and why it should be used when evaluating money in the future.
Discounting – what is it: the essence of the rate and method – Something like that!